
- Hard disk cloning software free bad sector how to#
- Hard disk cloning software free bad sector professional#
- Hard disk cloning software free bad sector download#
Hard disk cloning software free bad sector professional#
To complete that job, please upgrade to its Professional edition. ✿ AOMEI Backupper Standard edition does not support clone system disk between MBR and GPT partition style. ✿ The destination MBR disk will be overwritten or deleted during the sector by sector cloning process, please backup the critical data if you don’t want to lose them. Step 3. Select larger MBR disk as Destination Disk (here is disk 2).
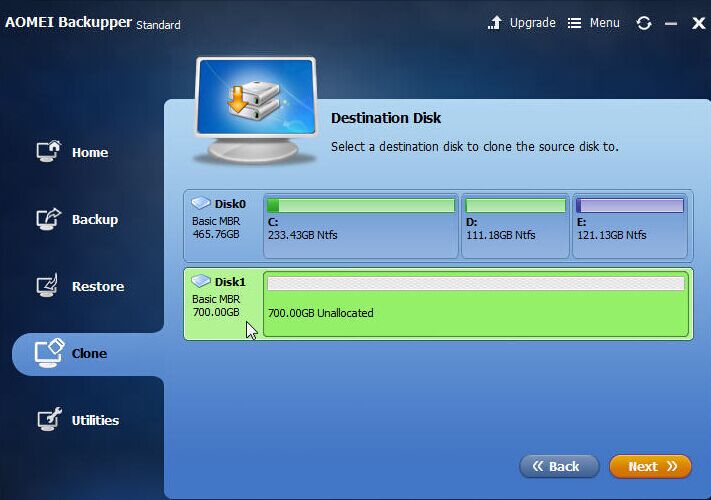
Step 2. Select the GPT disk you want to clone as the Source disk (here is disk 1), and click Next button. Step 1. Select Clone -> Disk Clone on the main console.
Hard disk cloning software free bad sector how to#
Now, we will show you how to clone sector by sector from a GPT data disk to larger MBR disk directly with AOMEI Backupper.
Hard disk cloning software free bad sector download#
The supported Windows operating system is Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8, 8.1, 10.įirst of all, please download AOMEI Backupper Standard and run this program. To clone disk sector by sector to HDD/SSD, the best free sector by sector clone software - AOMEI Backupper Standard will help you to clone easily, it provides the options to sector by sector clone or not.īesides, it’s available for you to clone HDD to smaller SSD as long as the used space is smaller than the destination disk, clone data partition to another, etc. Clone Disk Sector by sector with Free Sector by Sector Clone Software And Advanced Format Drives (AFD) use 4096 bytes per physical sector but emulate 512 bytes per logical sector. Generally speaking, the common hard drives (HDDs) owns 512 bytes per sector both on physical and logical sector, and 2048 bytes for CD-ROMs and DVD-ROMs.


it should say Bytes/Sector 4096 or Bytes/Sector 512, etc. It will show you the information of all drives on the right side.įind your desired drive and check the value for Bytes/Sector. Then go to System Summary -> Components -> Storage -> Disks. Run msinfo32 command to open System Information window.ģ. Press Win + R key combination to open Run dialog.Ģ. Value: 1: Enable Way 2: Check in System Informationġ. HKLM\CurrentControlSet\Services\\Parameters\Device\ Sometimes, you may get the Bytes Per Physical Sector : error, make sure that the following registry path exists to fix it: If you have the same value for Bytes Per Sector and Bytes per Physical Sector on both disks, then you could perform the sector by sector clone. Find the values for Bytes Per Sector and Bytes per Physical Sector to check the drive type that you have according to the Microsoft chart. Run the command prompt as an administrator:įsutil fsinfo ntfsinfo x: (the x: refers to the drive letter that you want to check)Ģ. How to verify the sector size for your source and destination disk before cloning? There are two ways to check: Way 1: Check from Command Promptġ. Because it’s not possible to copy one drive to another if the logical sector size of target drive differs from logical sector size of source drive.ĭestination disk/partition should be larger than or equal to the source disk/partition, or you will get failed due to the insufficient space on target location. If you are trying to perform the sector by sector clone, you have to check the following two things:Įnsure the logical sector size is the same on source and target disk.
The sector by sector clone is optional, you could try it or not. Check Sector Size Before Sector by Sector Clone Is sector by sector clone/backup is better? Actually, the sector by sector clone/backup makes no difference to a normal backup or clone. By the way, the sector is the smallest unit of disk access. Sector by sector clone (sector by sector copy) will clone all sectors on the source disk even if the sector is blank or it’s a logically bad sector to the destination hard disk (HDD/SSD), you will get the exact copy of a source disk/partition with the same properties like same drive status, drive capacity, drive letter and partitions on the target disk.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
